In today’s competitive business landscape, the ability to recruit efficiently and effectively is more crucial than ever. It is a misconception that recruiters’ and talent acquisition managers’ most important skills are their so-called “soft skills”. While the soft skills are still relevant, being good with numbers, not just people, is a must in recruitment today. Luckily, technology and software help recruiters gather and analyse the data, and streamline the recruitment process.
In this guide, we’ll delve into the world of recruitment metrics, offering insights into the best KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) to measure, track, and optimise your hiring process.
What are recruitment metrics?
Recruitment metrics are data points used to track the effectiveness and efficiency of your hiring process. Recruitment metrics can be divided into two categories: efficiency metrics and quality metrics.
Efficiency metrics measure the speed and cost-effectiveness of the recruitment process. These include ‘Time to Fill‘, which calculates the time from job posting to acceptance of an offer, and ‘Cost Per Hire‘, which accounts for all expenses associated with filling a role. A lower time to fill and cost per hire generally indicate a more efficient recruitment process.
On the other hand, quality metrics focus on the effectiveness and outcomes of the recruitment process. ‘Quality of Hire‘ is a prime example, often considered the holy grail of recruitment metrics, it gauges the value new hires bring to the organisation, including their performance, cultural fit, and longevity. Another important quality metric is the ‘Offer Acceptance Rate‘, reflecting the attractiveness of your job offers.
These metrics help HR professionals and hiring managers make informed decisions, improving the overall recruitment strategy. This article includes a list and explanations of the most useful recruitment metrics.

Why is measuring your recruitment metrics important?
Understanding your recruitment metrics is crucial for several reasons.
First, they provide visibility into how well your recruitment process is functioning. Are you filling roles quickly? Are you attracting high-quality candidates? Are new hires staying with the company? What are the bottlenecks in your process? You get a good indication of your performance and the strength of your strategy.
Second, recruitment metrics can highlight areas for improvement. For example, if the time to fill a role is longer than industry standards, it might signal a need for a more streamlined process. You can also compare recruitment for different roles within your company and pinpoint the roles which require more investment. These areas might change in time, so consistently measuring the same metrics helps you adjust the process agilely.
Lastly, these metrics can help you measure Return on Investment (ROI). For example, by understanding the cost per hire or the quality of hire, you can ensure that resources allocated to recruitment are well-spent. You can also measure, compare and evaluate your recruitment sources and identify the best sources for you. This way, you can allocate the budget to the most efficient sources and channels.
Choosing the best recruitment metrics to track
Choosing the right recruitment metrics to track for your company depends on several factors including your hiring goals, the nature of your business, and the challenges you’re currently facing in your recruitment process. Here are some steps to help you choose the right metrics:
1. Identify your recruitment goals: The first step is to clearly identify your recruitment goals. Are you looking to speed up your hiring process? Improve the quality of your hires? Increase diversity? Reduce hiring costs? Different goals will require different metrics.
2. Understand your business context: The nature of your business and industry will also influence which metrics are most relevant. For example, if you’re in a highly competitive industry for talent, time to hire might be a crucial metric. If you’re in a high-turnover industry, retention rate might be more important.
3. Review your current challenges: Look at the issues you’re currently facing in your recruitment process. If you’re struggling to fill roles quickly, you might want to track time to fill. If you’re getting a lot of applicants but few quality hires, you might want to look at quality of hire.
4. Consider your resources: Some metrics are harder to track and analyse than others. Make sure you have the resources and tools needed to accurately measure the metrics you choose.
5. Consult with stakeholders: Speak with key stakeholders such as hiring managers, other recruiters, and executives. Their insights can help you understand which metrics are most important for your company.
6. Benchmark against industry standards: Benchmarking your metrics against industry standards or similar companies can give you a sense of what you should be aiming for.
Remember, the metrics you choose should provide actionable insights that can help improve your recruitment process. They should be regularly reviewed and updated as your goals and challenges evolve.
Recruitment metrics best practices
When it comes to measuring recruitment metrics, here are a few best practices to follow:
Consistency: Ensure you’re measuring the same metrics consistently over time to track trends and progress.
Benchmarking: Compare your metrics with industry standards or similar companies to understand where you stand.
Actionability: Focus on metrics that can lead to actionable insights. If a metric doesn’t help you make better decisions, it might not be worth tracking.
Holistic Approach: Consider a wide range of metrics to get a complete picture. Focusing solely on one metric might lead to a skewed understanding of your recruitment process.
How to measure your recruitment metrics?
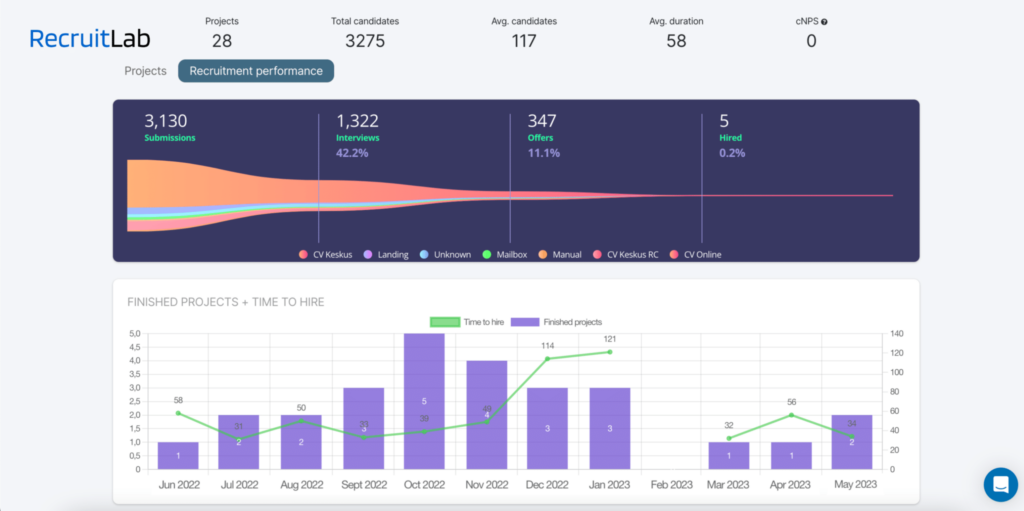
Recruitment metrics can be measured using various tools and techniques. HR software and Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) can automatically track many of these metrics.
An ATS automatically collects and organises data from your recruitment process, making it easy to track metrics like Time to Hire, Source of Hire, and Applicants per Role. An ATS can also visualise the data for you so you can get the information quickly and make decisions based on the data.
To measure metrics like Quality of Hire or Candidate Experience, you might need to use additional methods like performance reviews or candidate surveys. Surveys can be used to gather feedback or qualitative data from candidates and new hires, and data analytics can be employed to extract insights from the data.
Using data analysis techniques to interpret your metrics and extract actionable insights is also important. This might involve calculating averages, identifying trends, comparing against benchmarks, and so on. Remember, the key to measuring recruitment metrics effectively is to be consistent, accurate, and strategic, focusing on the metrics that align with your recruitment goals and challenges.
The most important recruitment metrics
Time to Fill
This metric represents the time it takes from posting a job opening to having an accepted offer. It helps measure the efficiency of your recruitment process. If the time to fill is lengthy, it might indicate bottlenecks or inefficiencies in your hiring process.
Time to Hire
Similar to time to fill, time to hire measures the period from when a candidate enters your pipeline to when they accept an offer. A longer time to hire can lead to losing candidates to other opportunities and can indicate areas for process improvement.
Candidate Net Promoter Score (cNPS)
The Candidate Net Promoter Score is a common metric many businesses use to gauge candidate satisfaction and loyalty. It’s determined by asking candidates a simple question: “On a scale of 0-10, how likely are you to recommend our company as a good place to work to a friend or colleague?” Based on their responses, customers are categorised as Detractors (0-6), Passives (7-8), and Promoters (9-10).
The cNPS is then calculated by subtracting the percentage of Detractors from the percentage of Promoters.
Candidate Diversity
Diversity metrics gauge the representation of different groups among your candidates and hires. It’s important to track these metrics to ensure fair hiring practices and foster a diverse and inclusive workplace.
Applicants per Role
This metric shows the number of candidates applying for each open position. A high number can indicate a desirable position or company, requiring an especially efficient process to find the most suitable candidate.
Application Completion Rate
The application completion rate is a metric that indicates the percentage of job applicants who start the application process and successfully complete and submit their application.
It’s a KPI for the efficiency and user-friendliness of a company’s job application process. If the completion rate is low, it may suggest that the application process is too lengthy, complex, or confusing, causing potential applicants to abandon their applications partway through. This could result in a company missing out on potentially qualified candidates.
To improve this rate, companies often improve their application forms by simplifying them, provide clear instructions, and ensure the application process is as streamlined and user-friendly as possible.
Offer Acceptance Rate
This is the ratio of job offers that are accepted compared to those made. A lower rate may suggest that your offers are not competitive in terms of salary, benefits, or other factors.
Quality of Hire
This is probably the most challenging recruitment metric to quantify accurately. It can include factors such as job performance, cultural fit, retention rate, and longevity with the company. Each of these factors can be difficult to measure, and there’s no universally accepted method for calculating overall hire quality. When you decide on the factors which work for your company, it is important to keep the measuring system consistent throughout the time analysed.
Cost of Hire
This includes all expenses related to hiring, such as advertising costs, recruiter fees, time spent by internal staff, and more. Keeping this cost low while still attracting quality candidates is a key goal for many recruiters.
Source of Hire
A recruitment metric that identifies where your candidates are coming from. This could include various channels such as job boards, social media platforms, company career pages, employee referrals, recruitment agencies, and so on.
Conclusion
In conclusion, recruitment metrics are not just numbers, they’re strategic tools that can help your company attract, hire, and retain top talent. By understanding your needs and choosing the best metrics according to them, you can continuously improve your recruitment process. There is a variety of metrics in use but not all of them are equally important to every company. Using an ATS automates the collection and analysis of the data, which allows you to make decisions based on them faster.
It’s all about getting the right people in the right roles at the right time. And in the end, that’s what great recruiting performance is all about.
Teamdash – The all-in-one recruitment software.
Streamline your recruitment process, save up to 70% of your time and hire top talent fast.